Last year, we discussed BI trends for 2022 by simply observing companies that rely heavily on analytics to become more efficient. While these companies had powerful and often expensive analytics tools at their disposal, the tools were never used to even half their potential. The result: disappointing returns on their data and analytics investments.
For 2023, this observation is more widespread. The economic pressure that companies are under is pushing them to rationalize their investments and maximize returns. According to Gartner, IT investments will only increase by 5.3% in 2023: less than the global inflation, which should reach 6.5%. Yet, according to EY's The CEO Imperative" study, 22% of CEOs see the use of data as a priority to develop their products and services. Data remains as important as ever, but ensuring its real impact on the business is becoming crucial.
According to another survey of 2,000 CIOs conducted by Gartner, 55% of those polled say they will continue to invest in data and analytics in 2023. According to Gartner, executives will be more demanding about the real impact of their investments. They will put in place precise metrics to evaluate the performance of their analytics. This focus on the performance of analytics and their real value has determined the 5 key trends we will see in 2023.
1. Adoption is the highest priority
Why does the ROI of BI and analytics tools continue to be disappointing for executives? From a technical point of view, the tools used to explore, model or analyze data continue to improve. But here's the thing: it's not just computing power that determines the real impact a BI tool will have on a company's bottom line.
The true metric to measure the effectiveness of BI and analytics tools is adoption. It's simple: no matter how much an executive invests in the most powerful analytics tools on the market, if no one in the company uses them, they're useless.
Adoption is not just about the data teams, who have the technical skills to use the most complex tools. For data to have a real impact within a company, it is necessary that all business lines consult it and adopt a truly data-driven approach, even those that are not technical: marketing, sales, HR...
This year, BARC and Eckerson Group conducted an international survey that revealed that adoption rates of analytics tools are stagnating at around 20%. In 2023, the market will make diagnosing low adoption its major priority and executives will be looking to drive their employees to use the analytics solutions the company has so heavily invested in. Analytics solutions that prioritize user experience, accessibility and mobilitywill be at the forefront of this change, with a heavy emphasis on embedded analytics.
2. Embedding analytics in tools and software
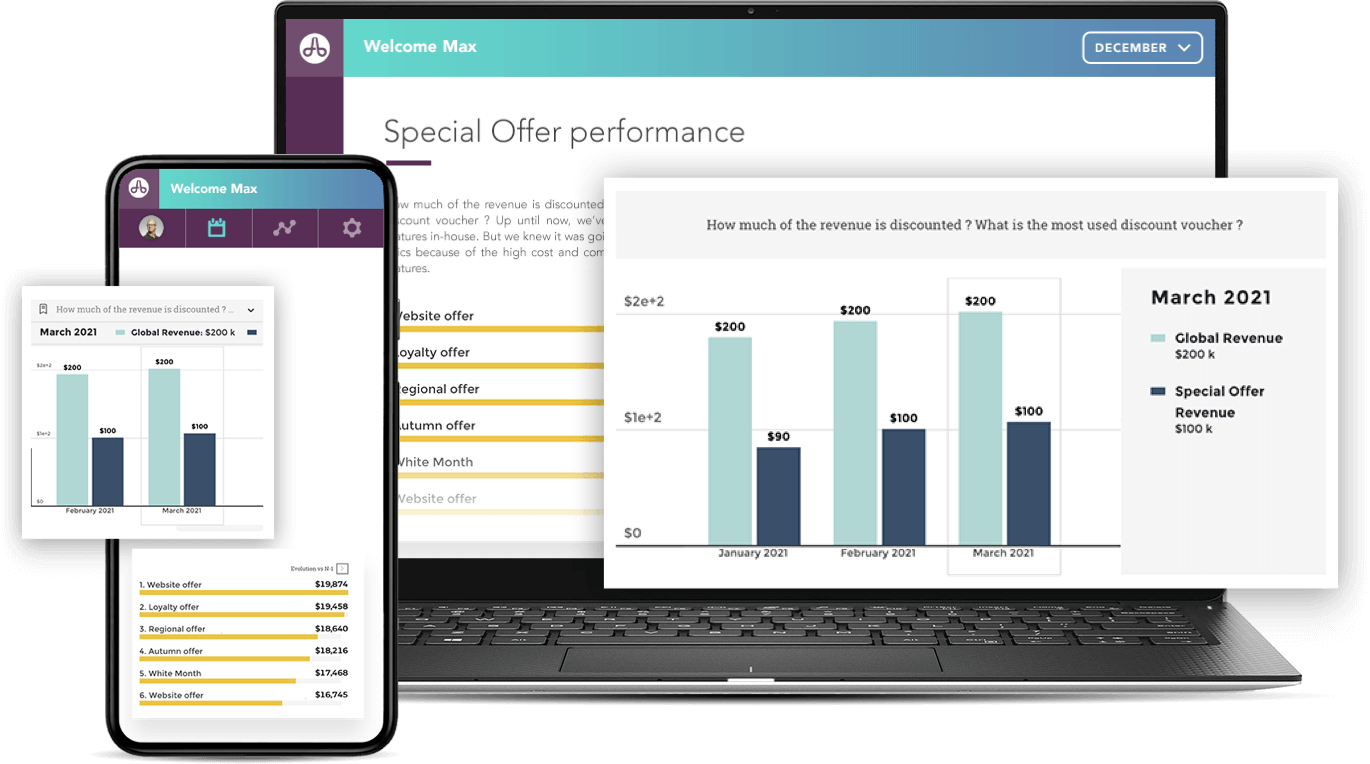
How do you get business users to regularly consult their analytics tools for actionable insights? Software companies are constantly improving their platforms to make it more user-friendly and increased the product's frequency of usage by making their business products as interactive as consumer applications. But that's not enough! For users, there is always a cost associated with moving from one ecosystem to another. Sales, Marketing, HR, Product or Finance teams already have their tools of choice that they use every day. While the user experience of analytics platforms is constantly improving, it will always take added effort to connect to and manipulate data in them.
This is where embedded analytics steps in. Rather than attracting business users to analytics platforms, we integrate analytics on their business platforms. For example, take analytics tables inserted into CRM, Sales or HR applications. The important thing is to display data at every step of the business users' workflow to help them make better decisions. Data is no longer thought of as an independent brick, but as a central ingredient that can be found throughout the user journey.
Embedded analytics is particularly important to SaaS companies, who are looking for a new functionality that can be easily integrated into their application. Their users gain added access within the product, at a glance, to key information, allowing them to understand their data and gain actionable insights. This is a way for SaaS companies to offer even more value to their users, in a short amount of time, while keeping their teams of developers focused on the core product.
3. Cloud conquers the market
Increasing the ROI of analytics and BI is the top priority for executives in 2023. This means that no executive can do without the technology that has revolutionized the industry: the cloud. Whether it's to store data or process it, companies will be less likely to rely on more expensive and high-maintenance local servers. Instead, they will rely on cloud servers. The proof is in the pudding: Amazon Web Services, Amazon's cloud computing provider, is up 33% in revenue over the previous year, despite the global economic climate.
Cloud servers have several advantages. First, the company using a cloud server does not have to worry about maintaining it. These services are usually offered as flexible subscriptions, and are therefore easily scalable. They can easily adapt to the needs of companies that face a rapid increase or decrease in activity. Finally, the most innovative and efficient databases are found in the cloud, for example, data warehouses, which are distinguished by their organization and ease of use. When companies store their data in cloud-based data warehouses, they also tend to rely on a fully cloud-hosted data stack for connectivity. This includes cloud analytics, which is expected to experience the same boom in 2023, especially since cloud analytics is proven-to-be more accessible, flexible and easy to use than on-premise solutions. This will help democratize analytics in the enterprise.
4. Concerns of digital sovereignty
Data is not just an economic issue. It is also geopolitical. In an uncertain international environment, the question of "digital sovereignty" is becoming increasingly important in Europe. While the cloud revolution has enabled companies to access more flexible and efficient services, it also raises the question of personal data surveillance.
Overturning the Data Privacy Shield by the European Court of Justice hasn't made software companies' lives any easier. Due to recent legal developments, the Shield is no longer valid. So, companies which have their headquarters in the US are no longer permitted to transfer data from the EU to the USA. A similar situation happened already in 2015 when the EU and the USA had no legally valid agreements on this matter for a while.
From a legal perspective, the US judiciary could force US-based businesses to even reveal data from EU-based servers. In essence, the information that is located in the EU needs to stay in the EU. In practice, that means that EU-based businesses that use, in the current situation, US-based software vendors that store any kind of data for them are taking chances as they operate in a legal gray area. For companies such as Toucan, this doesn't represent a big issue since the registration, business, and servers are located in the EU.
5. Rise of 3rd generation BI tools
In the field of analytics, things are moving fast. In just over a decade, three generations of BI tools have come onto the market. The first generation tools are the traditional tools that were designed exclusively for data scientists. Business users did not have access to them. In the early days of enterprise analytics, the democratization of data was not yet the priority it is today. To access data, non-expert users had to go through the data teams.
This is a problem that 2nd generation tools have tried to solve, by positioning themselves as "self-service" BI tools, more easily usable by all. The 2nd generation BI tools pioneered by focusing on data understanding and user experience. They rely on, for example, data visualization to enable users to draw the right conclusions from their data at a glance. While these self-service tools are designed to make data easier to understand, they give users little control over data sourcing. They don't know where the data comes from and can't select the sources themselves. For that, they still need the experts.
The 3rd generation tools aim to give business users complete autonomy in terms of data. From the selection of data sources to their activation, business users can create the analytics they need themselves. Thanks, in particular, to the progress of artificial intelligence, these "augmented BI" tools can translate requests made visually or in natural language by users into "coded" queries. No need to know how to code to analyze data. In 2023, this approach completely aligns with the priorities of executives who want their analytics to have a concrete impact on their results. This is why 3rd generation BI tools will the biggest trend in this coming year and decade.