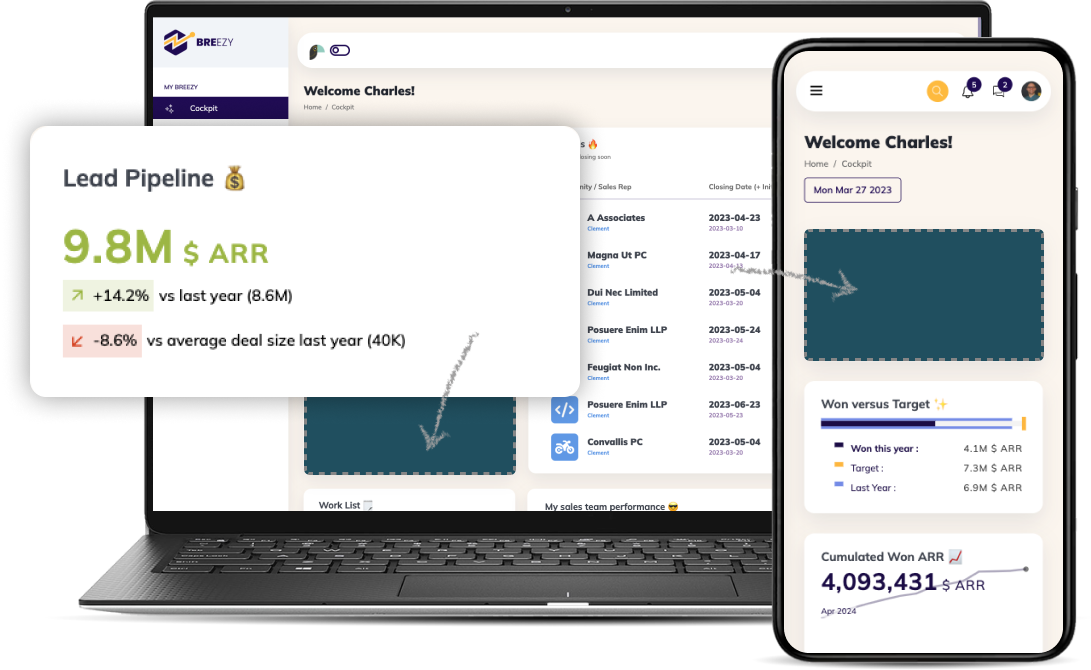
Cross-functional collaboration and communication happen when people with different skill sets and KPIs come together to work towards a greater goal, which is typically ROI-centric and critical to business success.
Product management is cross-functional by nature, with most product teams having a mix of engineers, designers, product managers, analysts, researchers, and other roles. Product teams collaborating cross-functionally can reduce churn rates and increase retention rates, increase product signups and activations, and increase MRR. To demonstrate this better let’s take a look at the case of Peter.
.png?width=600&name=Blog%20Graphics%20(18).png)
Peter is a product manager who works at a SaaS company. Recently Peter has noticed ower customer retention and higher churn. The numbers for both these important customer KPIs have been increasing over the last few months. Peter brings this up at the monthly review which is attended by his product team along with members of the marketing and customer service team. Upon reviewing the customer satisfaction metrics in detail Peter discovers that one category has constantly fallen short, that being the quality of customer service.
After the meeting, Peter pulled in customer service analytics shared by the team and realizes that the response time is abnormally high and almost 2x their industry average. Could this be a problem with insufficient personnel? Peter needed more insights to get the right information. The count of tickets showed that the customer service team was getting bombarded with questions about analytics in the application. They were unable to understand and quantify the impact that the product was having on their organization. Now having clearly understood that this is a product issue, with unanswered customer needs Peter races to add the feature. After consulting with the development team, he finds out it will take too long to build the analytics feature on their own, so he reached out to a third-party analytics solution, he reached out to Toucan.
After the first call, within 3 weeks Toucan is completely embedded within the product with all the analytics features and white-labeling to make it seamlessly blend in with the existing product. Within a month, Peter is able to notice a drop in the number of tickets coming in and better response times. At the next quarterly meeting, he is able to share with all teams that their churn has been cut in half and with an added analytics feature they have more customers and are able to charge an additional fee for upsell, overall increasing retention rates and revenue.
Important Cross-functional KPIs to Monitor for Product Managers
Products managers should track the following cross-functional product management KPIs:
1. WEEKLY TEAM MEETINGS
Each week, a team or group has a scheduled get-together at a designated time. The weekly meetings are important because they tend to address action items, roadblocks, and questions for the upcoming week. As a result of regular meetings, team members are able to progress with their weekly tasks. There are a number of potential roadblocks that prevent successful meetings, regardless of whether your team is remote. Bad communications cannot be overcome by great technology. Incorporate all critical steps into the project management plan and make sure that all team members are on board and accepting the plan.
- How does the testing process work?
- What phases are approved by whom?
- Is it necessary to involve cross-functional teams?
Even a technology-driven plan can be thrown off by internal disorganization. This can occur at the onset of the project and goes back to communication barriers associated with remote collaboration. Set up a call to discuss the organizational structure of the remote team and how the team will engage with one another.
2. MONTHLY / QUARTERLY OPS REVIEWS
The purpose of an operational review is to examine a particular segment or an entire organization in depth and objectively. In addition to identifying and addressing existing concerns within your company, it can help you to identify and address operational procedures, customer relations issues, business stability issues, and other factors.
Organizational reviews enable members to evaluate the effectiveness of their operation if they are performing as per the procedures set by the organization, allocating resources effectively, and completing such tasks within the set time frame and using cost-effective methods. In addition, it shows your organization's readiness to face future challenges.
What should be included in an operational review
- Assess compliance within your own organizational objectives, policies, and procedures
- Evaluate specific company operations independently and objectively
- Impartial assessment regarding the effectiveness of an organization’s control systems
- Identify the appropriate standards for quantifying the achievement of organizational objectives
- Evaluate the reliability and value of the company’s management data and reports
- Pinpoint problem areas and their underlying causes
- Identify opportunities to increase profit, augment revenue, and reduce costs without sacrificing the quality of the product or service.
3. LEAD GENERATION
Your sales team can handle lead generation efforts, marketing department, or product team. The most qualified leads need to be defined and segmented when you have complex sales funnels.
Qualified leads fall into three categories.
- Marketing qualified leads (MQLs): Marketing qualified leads are customers who have engaged with your marketing team but are not ready to receive a sales call.
- Sales qualified leads (SQLs): These are customers who have taken actions that express their interest in becoming paying customers.
- Product qualified leads (PQLs): Product qualified leads are those who have used your product and shown interest in becoming a paying customer.
The two main ways to assess if a lead is more likely to become a customer are:
- Grading - Using your customer personas, you identify prospective buyers interested in your products and services and focus specifically on B2B.
- Marketing - Using landing pages, you grab visitors' attention and capture their email addresses. As a result, they expect more interaction with your brand.
4. CONVERSION RATE
Conversion rate is a product management KPI with relevance in the lead lifecycle. This KPI measures the proportion of leads that continue along the funnel to become customers. Conversion rates help you understand how many leads you need to bring into the funnel to achieve your goals and find major areas of customer drop and reasons customers do not continue down the sales cycle.
The formula for conversion rate is as follows:
- Conversion rate = (the number of users that become paying customers) x 100/the total number of users
5. COUNT OF TICKETS
Count of Tickets or Total Tickets tracks all tickets in your support queue over a period of time. A variation of this metric is Total Conversations, which counts all customer engagement, including official support tickets, tweets, and other social media.
Support software usually distinguishes between tickets and conversations. In some cases, every conversation is automatically recorded as a ticket, whereas in others, only tickets that are created through your website or help center are displayed as tickets. For example, you can track email support tickets, help center tickets, Facebook tickets, and Twitter tickets. Regardless of which version you track, these metrics indicate the current demand on your support team.
The formula for the count of tickets is as follows:
- Count of tickets = Sum of all tickets received in a given period of time
6. CUSTOMER SATISFACTION (CSAT)
Among product management metrics, customer satisfaction (CSAT) helps you measure the overall customer experience. All companies including enterprises, start-ups, SaaS companies, etc. can use this measurable indicator.
Customer satisfaction is commonly measured by designing questions that cover all aspects of the user experience. By analyzing the customer satisfaction score and detailed responses companies can see which customers are unhappy, and subsequently, take corrective actions
The formula for customer satisfaction is as follows:
- CSAT = (the number of positive responses from customers) x 100/the total number of survey responses
7. RETENTION RATE
Customer retention rate is an important product management KPI for you to measure customer loyalty. Different stakeholders like sales teams and product teams in organizations can use this KPI. Drop in customer retention rate indicates that users are not happy with the product and can find better alternatives in the market.
The formula for retention rate is as follows:
- Retention rate = {(the total number of customers at the end of a time period – the number of new customers onboarded during this period) x 100}/the total number of customers at beginning of the period
8. CUSTOMER CHURN RATE
Customer churn rate is a product management KPI to measure how many customers you lose. You might lose some customers due to various reasons, e.g., they didn’t like the new features introduced. Churn rate is inversely related to retention rate. You want to keep churn low and ensure businesses stay with you longer proving the usefulness of your product to future prospects.
The formula for churn rate is as follows:
- Churn rate = (the number of customers lost during a specific time period) x 100 / the total number of customers at the beginning of the period
9. ESCALATION RATE
Escalation Rate is the percentage of support tickets that have been escalated to a new support tier. In some cases, you may escalate vertically to a senior colleague, or horizontally to more teammates for assistance or advice – even to someone who has the relevant expertise in another department. The Escalation Rate can also be broken down into the number of tickets escalated through your company's support tiers or the number of tickets escalated by different team members. Escalation rates can be calculated and tracked on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis.
The formula for escalation rate is as follows:
- Escalation Rate = Number Support Tickets Escalated From First Tier / Total Number Of Support Tickets
10. First Response time
Your First Response Time (FRT) plays a crucial role in determining the levels of customer satisfaction. First reply time is more important than overall reply times because it’s an acknowledgment to the customer that their issue is being looked into.
In most cases, if you lower the time taken to respond to queries, the higher the level of customer satisfaction. Different support channels also come with different expectations of response times. In terms of industry benchmarks, customers contacting you by email generally expect a response within 24 hours. For social, the recommended benchmark is to respond in 60 minutes or less. For phones, the generally accepted response time is three minutes. It’s important to look at the trend of average first response time to check whether it’s increasing or decreasing over a period.
It’s also good practice to work with your team to find your “Goldilocks Zone”, where you set a balanced FRT target that enables your team to reply to customers in good time but not to the point where it becomes stressful and impacts the quality of their responses.
There you have it! This is by no means a comprehensive list of cross-functional metrics you could be tracking during the product management process, but it is certainly enough to get you started with some ideas. Project management is an iterative process that needs to be continuously implemented and checked. The best way to do this is by using an analytics solution that can give you all the information at a glance so that you don't have to go around digging for the insights you need. Try out toucan to see how the HKPIs, color-coded metrics, and guided analytics change how you manage projects.