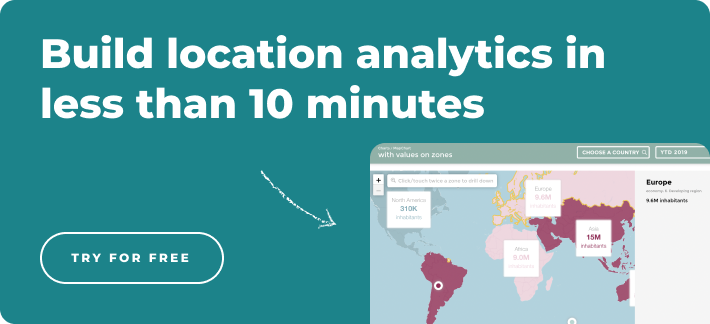
Location analytics - what is it?
Location analytics involves adding a layer of geographic data to a business's data assets in order to extract more valuable information. In some industries, business data, including information on people, events, transactions, assets, etc., often include a geographical component, which, when incorporated into an analysis of performance, may yield new insights. With this information, it is possible to ask questions about different business processes in a more contextual manner, offering a more complete understanding of trends and relationships within the data.
An organization can benefit from location analytics by providing employees with spatial analytics and other analytical capabilities for analyzing data from a location-specific perspective, making predictions, and optimizing their business practices accordingly. Incorporating location into an organization's analytics allows for greater context in decision-making and speeds the discovery of insights not available from traditional, flat business intelligence (BI).
In addition, maps provide unique insights into location data and are particularly easy to understand for non-experts. Traditional analytical tools such as statistical plots, charts, and tables would not be able to accomplish this. A location analytics platform can assist businesses in making better decisions based on geospatial data in a variety of ways, including optimizing operations across different territories, matching assets to resources, as well as test the profitability of potential new locations.
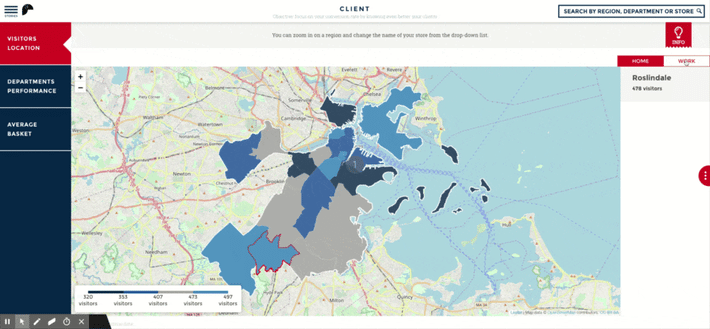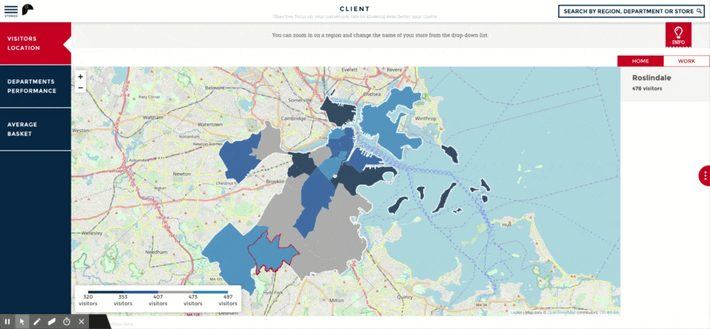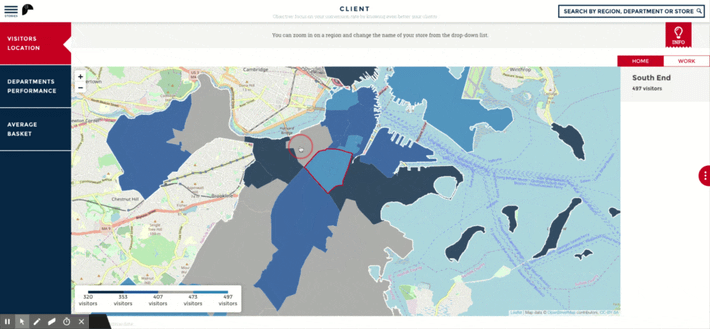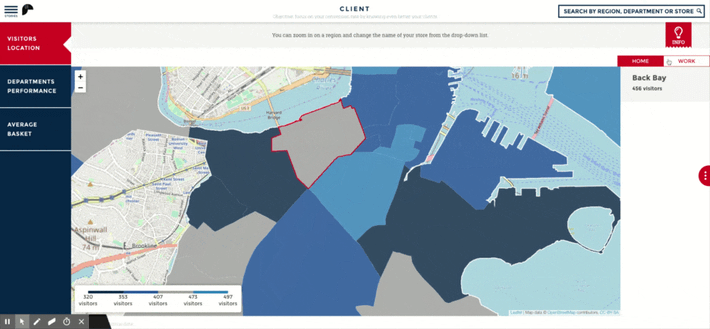
What are the Benefits of Location Analytics?
The ability to understand geospatial impacts on the business is essential in today's global economy. Businesses that utilize location analytics to assess their business strategies can reduce their costs, identify new sales opportunities, and improve operational efficiency. Additionally, location analytics is characterized by a high level of visual appeal, making it easier for non-technical business users to grasp the significance of the input data. As a result, those insights can be communicated to other departments and teams within the organization and can be more readily applied. Implementing location analytics provides three key benefits:
- Hyper-local Intelligence: You can use location analytics to turn data into location-based insights and communicate with business users, analysts, scientists, and developers using beautiful, location-aware visualizations for Geographic Information Systems (GIS). The improved management of information leads to improved collaboration between teams, which helps everyone in the organization make better decisions, often resulting in an increase in revenue and a reduction in costs.
- Real-World Context: Unlike many other information visualizations, maps connect data to the real world, clearly displaying how location is related to other data characteristics. The context provided by this information enhances the insights obtained by analytics teams and end users as they drill down into visualizations. There is no better way to add context and answer questions related to "where." A greater understanding of the location will enable organizations to identify new opportunities and optimize operations.
- Actionable Insights: In contrast to other GIS tools, location analytics promotes quick and easy creation of insightful geographical analyses. It will still provide the depth of analytical capabilities necessary for predictive analysis and other optimizations due to location. It is a win-win situation.
What are the main features of location analytics?
Interoperability
It has historically been only certain business functions and audiences that have been using location analytics in organizations. By integrating data from multiple systems and devices, newer location analytics platforms, like Toucan, aim to solve this problem. Toucan brings location analytics to your users with customer-facing embedded analytics.
By integrating all location analytics functions from multiple vendors into a single management interface, location analytics can realize its full potential.
Data collection
A location analytics system relies on data collected from LANs (local area networks), environmental sensors, cameras, network equipment, RFID tags, motion sensors, and telemetry. A data collection system is beneficial for tracking the products and produce in food services that are distributed throughout the facility. Toucan has interactions with over 100 databases making data collection easy and efficient.
Analysis
Once the data has been collected, it is analyzed and subjected to algorithms or rules that are designed to achieve certain business outcomes, safety outcomes, or environmental outcomes. Identifying patterns in customer foot traffic, for example, could lead to the rearrangement of product displays at a retail store in an effort to increase sales.
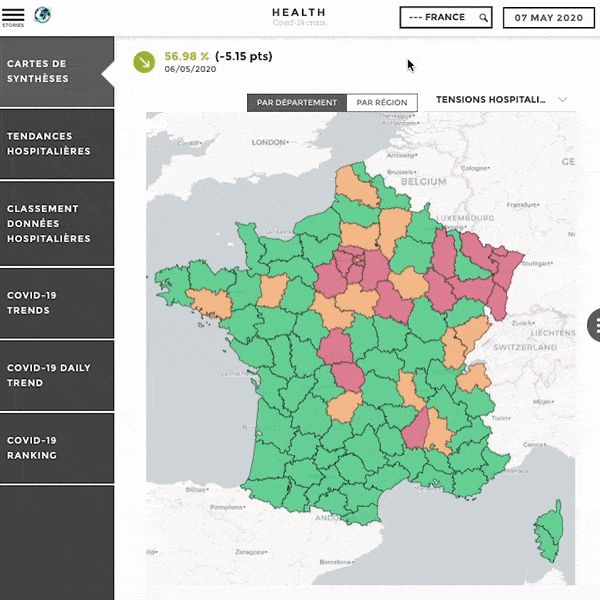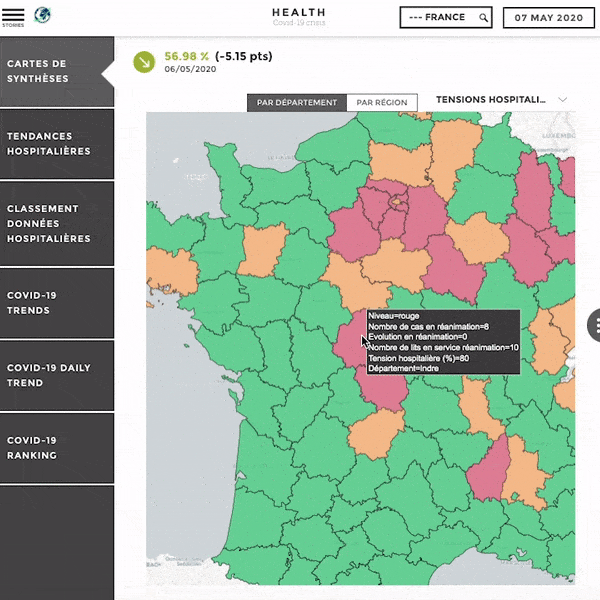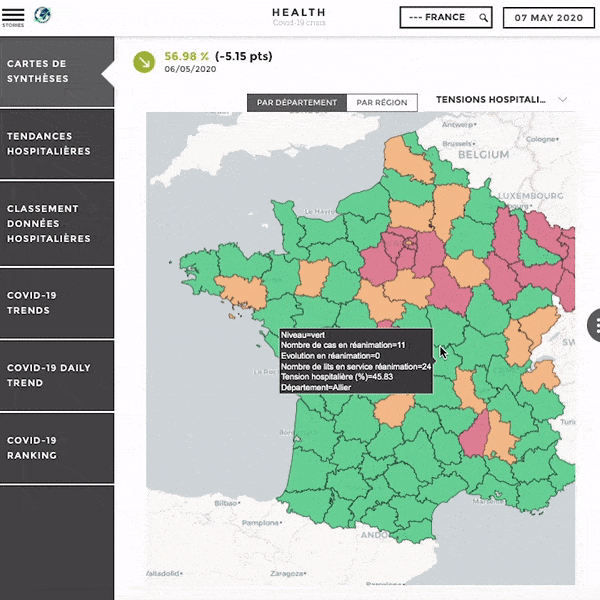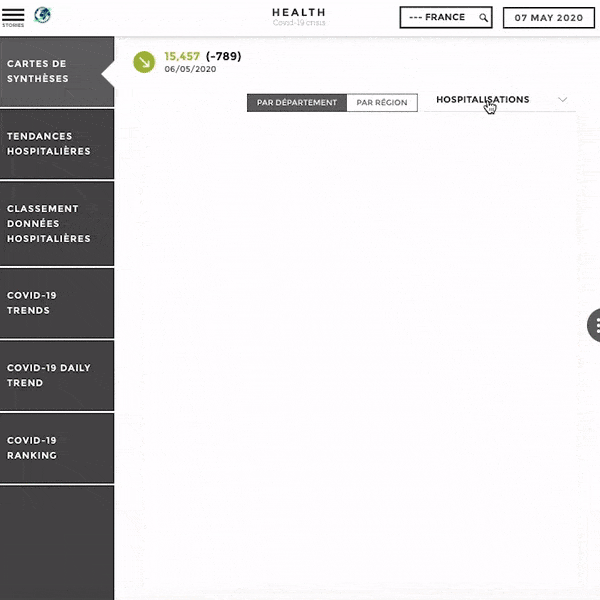
Customization
Location analytics solutions can be used to create custom content, such as real-time statistics on digital signage based on insights gathered, or pushing custom content to mobile devices. Long-term insights gained from location analytics may be applied in some cases, like reformulating business hours and offerings in the food/retail space based on time and frequency of foot traffic.
How Do Different Businesses Use Location Analytics?
Businesses can benefit from location analytics across a variety of industries. From manufacturing to assembly, logistics to distribution, location analytics can improve business processes from start to finish. By utilizing geographical data, it is also possible to enhance marketing strategies by better targeting the right people, making relevant offers in real-time, and understanding the needs of customers. In addition, it has become increasingly popular to target customers with personalized content.
In most business processes, location plays a significant role. Business data is inextricably linked to location, from financial transactions to stock transactions to location tracking. It is becoming increasingly common for organizations to utilize their location data. A number of recent technological developments rely on location analytics, such as smart cities, connected vehicles, the Internet of Things, and smart factories.
The use of location analytics can also be used to identify locations that businesses may want to target. Based on demographic data, optimize resource allocation by analyzing localized needs, as well as to make predictions based on historical and real-time data trends regarding future business and market trends. Thus, businesses and their customers can monitor, analyze, and make decisions within a geographic context at the right time.